Global Health Care Group

 Two ELISA test kits (based on monoclonal antibodies) are available for the determination of pancreatic
elastase 1.
Two ELISA test kits (based on monoclonal antibodies) are available for the determination of pancreatic
elastase 1.
The stool test quantifies E1 in stool, allowing the diagnosis or exclusion of pancreatic exocrine
insufficiency, which can be caused by chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, pancreatic tumor,
cholelithiasis or diabetes mellitus for example.
The serum test quantifies E1 in serum, allowing the diagnosis or exclusion of an acute pancreatitis or
an inflammatory episode of chronic pancreatitis or ERCP- or gallstone-induced pancreatitis.
Abdominal Pain – Maldigestion – Malassimilation – Chronic Pancreatitis – Cystic Fibrosis –
Post-traumatic injuries
Is the pancreas involved?
The reliable and cost-effective ScheBo® • Pancreatic Elastase 1™ Stool Test gives you the
answer.
The test is the new gold standard for non-invasive pancreatic function testing. It has been evaluated in comparisons with the invasive secretin-pancreozymin and secretin-caerulein tests.
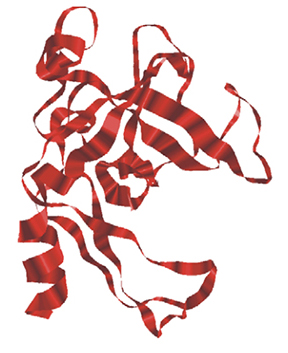
Human pancreatic elastase 1 (E1) remains undegraded during intestinal transit.
Therefore, its concentration in faeces reflects pancreatic exocrine function.
The diagnostic efficiency of pancreatic elastase 1 determination in stool has been evaluated in
several clinical studies. Stein et al. (1993 &1996, 1997) and Löser et al. (1995 &1996) compared the
E1 determination with invasive intubation tests, the secretin-pancreozymin test and the
secretin-caerulein test, respectively. Both authors report a sensitivity and specificity greater
than 90% for the diagnosis of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency.
In contrast to the fecal chymotrypsin assay, even a moderate pancreatic insufficiency can be
detected by E1 determination (Löser et al., 1995 &1996, Gullo et al., 1999).
In addition, studies by Terbrack et al. (1996), Soldan et al. (1996), Gullo et al. (1999), Wallis et
al. (1997), Walkowiak et al. (1999) and Cade et al. (2000) showed an excellent sensitivity and
specificity for the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis with pancreatic involvement.
References/literature download
Please find here selected literature as download. The complete list of references is to be found on the website “reply fax, request for references/literature”.
